NOTE: Article in Progress
1. Web Services
Web services
1.1. Introduction
.svg.png)
- Human-machine interaction
- client-server architecture
- URL rewriting
- Machine-machine interaction
- REST architecture style
- API documentation
Interaction homme-machine
Human-machine interaction
- Communication avec une machine (un PC ou un portable)
- Modes d'interaction (modes écrit, gestuel, visuel, parlé)
- Utilisation de plusieurs machines
- Communication entre les machines en utilisant des protocoles
- TCP/IP
- UDP
- Plusieurs configurations possibles
- Architecture client-serveur
- Répartition des tâches entre machines
- Client envoie des requêtes
- Serveur répond aux requêtes
- Identification des machines
- Dépasser les limitations d'une seule machine
- Protocoles de communication client-serveur
- FTP
- HTTP
- SMTP
- Identification et localisation des multiples ressources
- Utilisation des marque-pages par l'utilisateur
- Réduction d'URL
- Redirection d'URL
1.2 URL choice
URL
https://www.example.com/index.html
ou
https://www.example.com/index.php
ou
https://www.example.com/
https://www.example.com/index.php?lang=fr
https://www.example.com/index.php?lang=en
https://www.example.com/index.php?lang=es
ou
https://www.example.com/fr/index.php
https://www.example.com/en/index.php
https://www.example.com/es/index.php
https://www.example.com/fr/index.php
https://www.example.com/en/index.php
https://www.example.com/es/index.php
ou
https://www.example.com/fr/
https://www.example.com/en/
https://www.example.com/es/
https://www.example.com/index.php?operation=listStudents
ou
https://www.example.com/students/
https://www.example.com/index.php?operation=showStudent
https://www.example.com/index.php?operation=AddStudent
https://www.example.com/index.php?operation=deleteStudent
https://www.example.com/index.php?operation=updateStudent
ou
https://www.example.com/students/1/
1.3.URL rewriting
.svg.png)
Installation d'apache
$ sudo apt install apache2 php7.0 libapache2-mod-php7.0
Activation de réécriture
$ sudo a2enmod rewrite
$ sudo service apache2 restart
Vérification
<?php
phpinfo()
?>
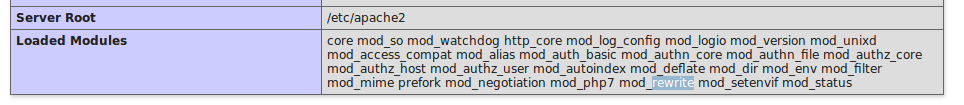
Configuration (Activation des fichiers .htaccess)
Vérifier le fichier /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
..
<Directory "/var/www/html">
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
Redémarrer apache2
$ sudo service apache2 restart
Redirection transparente vers index.php
.htaccess
DirectoryIndex index.php
- https://example.com/ est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/index.php
- https://example.com/fr/ est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/fr/index.php
Redirection transparente vers index.php
.htaccess
DirectoryIndex accueil.php
- https://example.com/ est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/accueil.php
- https://example.com/fr/ est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/fr/accueil.php
Redirection transparente vers index.php
.htaccess
DirectoryIndex accueil.php index.php
- https://example.com/ est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/accueil.php, si présent, sinon
- https://example.com/ est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/index.php
.htaccess
RewriteEngine on
RewriteRule ^test.html$ /index.php
- https://example.com/test.html est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/index.php
.htaccess
RewriteEngine on
RewriteRule "^.+.html$" /index.php
- https://example.com/abc.html est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/index.php
- https://example.com/abcd.html est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/index.php
.htaccess
RewriteEngine on
ErrorDocument 404 /404.php
RewriteRule "^(.+)/index.php$" /index.php?lang=$1
- https://example.com/fr/index.php est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/index.php avec des arguments lang=fr
- https://example.com/en/index.php est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/index.php avec des arguments lang=en
.htaccess
RewriteEngine on
RewriteRule "^(.+)/index.html$" /index.php?lang=$1
- https://example.com/fr/index.html est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/index.php avec des arguments lang=fr
- https://example.com/en/index.html est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/index.php avec des arguments lang=en
.htaccess
RewriteEngine on
RewriteRule ^students/(.+)/$ /students/index.php?id=$1
RewriteRule ^students/(.+)/(.+)$ /students/index.php?id=$1¶m=$2
- https://example.com/students/1/ est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/students/index.php avec des arguments id=1
- https://example.com/students/1/module1/ est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/students/index.php avec des arguments id=1 et param=module1
Erreur ressource non trouvée
.htaccess
RewriteEngine on
ErrorDocument 404 /404.php
- Les liens inexistants sont redirigés vers le lien https://example.com/404.php
1.4. Retrieving values from a HTML form
<fieldset>
<legend>Etudiant.e</legend>
<div>
<label for="nom">Nom</label><input type="text" id="nom" name="nom"/>
</div> <div>
<label for="prenom">Prénom</label><input type="text" name="prenom"/>
</div> <div>
<label for="prenom">Diplôme</label>
<select id="diplome" name="diplome">
<option>IRC</option>
<option>ETI</option>
</select>
</div>
</fieldset>
Récupération des valeurs
method="get"
<form action=request.php" method="get" >
<fieldset>
...
</fieldset>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
<?php
$method = $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'];
echo "method: ".$method;
?>
method="get"
<form action=request.php" method="get" >
<fieldset>
...
</fieldset>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
URL (navigateur) et l'affichage sur le serveur
http://localhost/request.php?nom=aple&prenom=mango&diplome=IRC
method: GET
method="post"
<form action=request.php" method="post" >
<fieldset>
...
</fieldset>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
URL (navigateur) et l'affichage sur le serveur
http://localhost/request.php
method: POST
method="put"
<form action=request.php" method="PUT" >
<fieldset>
...
</fieldset>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
URL (navigateur) et l'affichage sur le serveur
http://localhost/request.php?nom=aple&prenom=mango&diplome=IRC
method: GET
method="delete"
<form action=request.php" method="delete" >
<fieldset>
...
</fieldset>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
URL (navigateur) et l'affichage sur le serveur
http://localhost/request.php?nom=aple&prenom=mango&diplome=IRC
method: GET
1.5. Example
.htaccess
RewriteEngine on
ErrorDocument 404 /404.php
RewriteRule "^(.+)/index.php$" /index.php?lang=$1
- https://example.com/fr/index.php est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/index.php avec des arguments lang=fr
- https://example.com/en/index.php est redirigé vers le lien https://example.com/index.php avec des arguments lang=en
Récupération des valeurs GET: PHP
<?php
$language = "fr";
if($_GET["lang"]) {
$language = $_GET["lang"];
}
if($language == "en") {
echo "Hello!";
}
else if($language == "fr") {
echo "Bonjour!";
}
?>
Récupération des valeurs GET: PHP
<?php
if($_GET["nom"] &&
$_GET["prenom"] ) {
echo "Bonjour! ".$_GET["prenom"]." ".$_GET["nom"];
}
?>
POST: PHP
<?php
if($_POST["nom"] &&
$_POST["prenom"] ) {
echo "Bonjour! ".$_POST["prenom"]." ".$_POST["nom"];
}
?>
PUT, DELETE: PHP
<?php
if($_GET["nom"] &&
$_GET["prenom"] ) {
echo "Bonjour! ".$_GET["prenom"]." ".$_GET["nom"];
}
?>
GET, POST, PUT, DELETE: PHP
<?php
if(strcasecmp($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"], "POST") == 0) {
if($_POST["nom"] &&
$_POST["prenom"] ) {
echo "Bonjour! ".$_POST["prenom"]." ".$_POST["nom"];
}
}
else {
if($_GET["nom"] &&
$_GET["prenom"] ) {
echo "Bonjour! ".$_GET["prenom"]." ".$_GET["nom"];
}
}
?>
1.6. Debugging: Logging
Enregistrement de données (Serveur Apache)
$ tail /var/log/apache2/access.log
127.0.0.1 - - [14/Nov/2018:14:46:49 +0100] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 3477 "-"
"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:63.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/63.0"
127.0.0.1 - - [14/Nov/2018:14:46:49 +0100] "GET /icons/ubuntu-logo.png HTTP/1.1" 304 180 "http://localhost/"
"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:63.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/63.0"
127.0.0.1 - - [14/Nov/2018:14:46:49 +0100] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 294 "-"
"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:63.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/63.0"
$ tail /var/log/apache2/error.log
[Wed Nov 14 09:53:39.563044 2018] [mpm_prefork:notice] [pid 849]
AH00163: Apache/2.4.29 (Ubuntu) configured -- resuming normal operations
[Wed Nov 14 09:53:39.563066 2018] [core:notice] [pid 849]
AH00094: Command line: '/usr/sbin/apache2'
[Wed Nov 14 11:35:35.060638 2018] [mpm_prefork:notice] [pid 849]
AH00169: caught SIGTERM, shutting down
2. REST architecture style
- Interaction machine à machine
- Composants faiblement couplés
- Interopérabilité entre les machines
- Vers des systèmes totalement autonomes
- Representational state transfer
- Un style d'architecture pour les systèmes hypermédia distribués
- Proposé par Roy Fielding en 2000
- Interface machine à machine
2.1. REST: Contraintes
Une architecture REST doit respecter les six contraintes suivantes
- un architecture client-serveur
- Un serveur sans état
- Avec cache
- À interface uniforme
- En couches
- Code à la demande (facultatif)
1. Architecture client-serveur
2. Un serveur sans état
- La communication s'effectue sans conservation de l'état de la session sur le serveur
- Les requêtes contiennent toute l'information
- Amélioration de l'extensibilité du système
3. Avec cache
- Les clients peuvent mettre en cache les réponses (par exemple: cache du navigateur)
- Les serveurs peuvent mettre en cache les réponses (par exemple: memcache pour les requêtes
fréquemment posées)
- Amélioration de l'extensibilité et la performance du système
4. À interface uniforme
- simplifie et découple l'architecture
- permet à chaque composant d'évoluer indépendamment
4. À interface uniforme
- identification des ressources
- manipulation des ressources par des représentations (XML, JSON etc.)
- messages auto-descriptifs
- hypermédia comme moteur d'état de l'application
4. À interface uniforme
Hypermédia en tant que moteur de l'état d'application
Un client REST n'a besoin d'aucune connaissance préalable sur la façon d'interagir avec une application ou un serveur particulier au-delà d'une compréhension générique de l'hypermédia.
5. En couches
- Un client ne peut pas dire s'il est connecté directement au serveur final ou à un serveur intermédiaire.
- permet d'ajouter des équilibreurs de charge
6. Code à la demande (facultatif)
- Les serveurs peuvent temporairement étendre ou modifier les fonctionnalités d'un client en lui transférant du code exécutable.
- Exemples: Applets Java, scripts Javascript
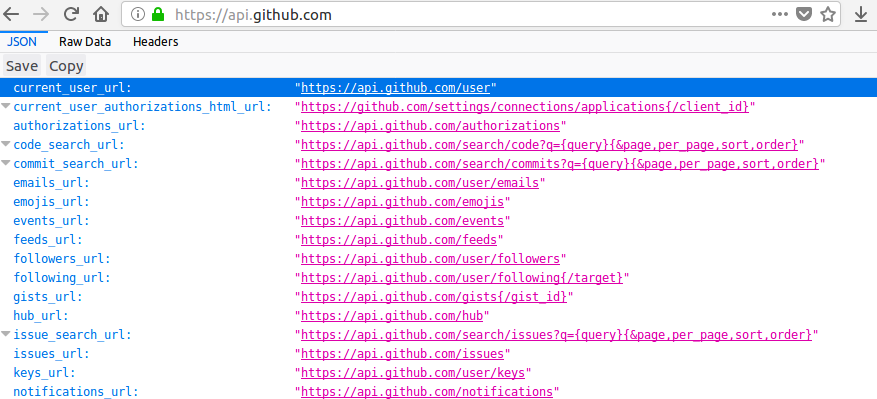
API Github (REST)
RESTful Services Web
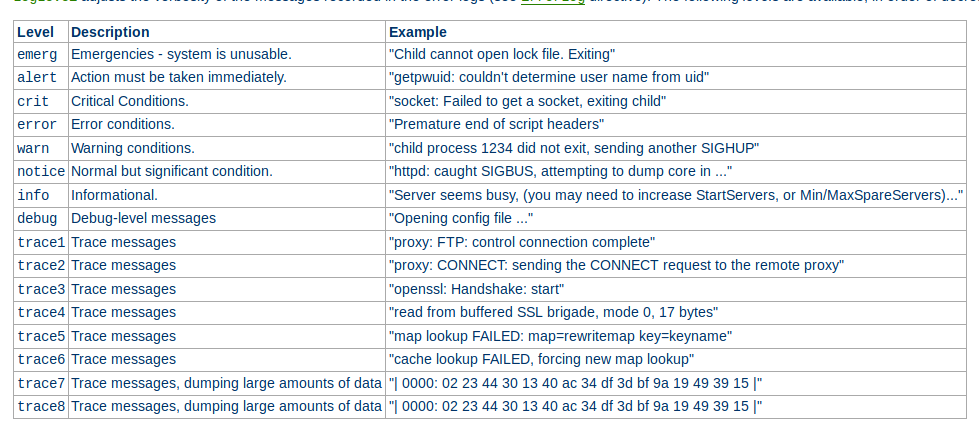
Différents niveaux [2]
- Niveau 0: HTTP
- Niveau 1: Ressources
- Niveau 2: Verbs HTTP (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
- Niveau 3: Hypermedia
https://www.example.com/students/
https://www.example.com/students/1/
https://www.example.com/students/1/module1/
2.2. HTTP codes
Liste des codes HTTP
- 1xx - Information
- 2xx - Succès
- 3xx - Redirection
- 4xx - Erreur du client web
- 5xx - Erreur du serveur / du serveur d'application
Liste des codes HTTP
Les codes les plus courants sont :
- 200 : succès de la requête ;
- 301 et 302 : redirection, respectivement permanente et temporaire ;
- 401 : utilisateur non authentifié ;
- 403 : accès refusé ;
- 404 : page non trouvée ;
- 500 et 503 : erreur serveur ;
- 504 : le serveur n'a pas répondu.
2.3. Creating RESTful API
cURL
- client URL request library : « bibliothèque de requêtes aux URL pour les clients »
$ curl example.com
cURL: en-tête (header)
$ curl -I http://localhost/index.php
Sortie
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Thu, 26 Apr 2018 18:54:18 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.18 (Ubuntu)
Content-Length: 14
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
cURL: GET
$ curl http://localhost/index.php
$ curl -X GET http://localhost/index.php
cURL: POST
$ curl -X POST http://localhost/index.php
$ curl -X POST --data 'user:abc' http://localhost/index.php
$ curl -X POST -d @file.json http://localhost/index.php
cURL: PUT
$ curl -X PUT http://localhost/index.php
$ curl -X PUT --data '' http://localhost/index.php
$ curl -X PUT -d @file.json http://localhost/index.php
cURL: DELETE
$ curl -X DELETE http://localhost/index.php
méthode HTTP
$_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD']
PHP: récupération de paramètres
$data = json_decode(file_get_contents('php://input'), true);
PHP:
echo http_response_code(521);
.htaccess
RewriteEngine on
ErrorDocument 404 /404.php
RewriteRule ^(.+)/$ /index.php?resource=$1
RewriteRule ^(.+)/(.+)$ /index.php?resource=$1&id=$2
3. API Documentation

API Documenation
- Documentation lisible par l'homme
- Documentation lisible par machine
- Documentation lisible par l'homme et machine
Documentation lisible par l'homme: Développeur/Développeuse

- lit la documentation de l'API en format texte ou HTML
- développe du code pour l'intégration avec les services Web
- ajoute code métier

Documentation lisible par l'homme: Développeur/Développeuse
- surveille les changements de l'API
- Réécrit le code si l'API change
API
- liste des opérations (méthodes)
- paramètres d'entrée et de sortie
- erreurs
- format du messagei (json, xml etc.)
- mécanisme d'authentification
- mécanisme d'autorisation
Documentation lisible par machine: WSDL
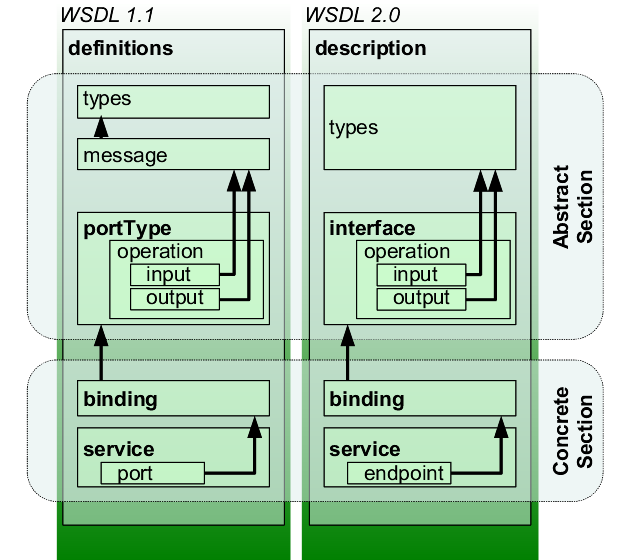
Le WSDL (Web Services Description Language) sert à décrire
- le protocole de communication (SOAP RPC ou SOAP orienté message)
- les méthodes (opérations)
- le format de messages (les types de données)
- la localisation du service


WSDL Libraries
- Java: wsimport, WSDL4J,..
- Python: zeep,..
WADL (Web Application Description Language)
- décrit des applications REST
- décrit des ressources, méthodes, paramètres et réponses

SA-WSDL (Semantic Annotations for WSDL and XML Schema)
- définit un ensemble d'attributs d'extension pour WSDL et XSD
- permet des annotations sémantiques en utilisant des ontologies
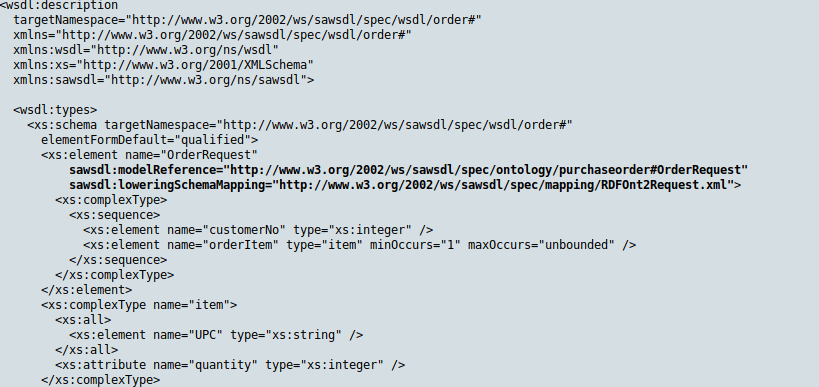
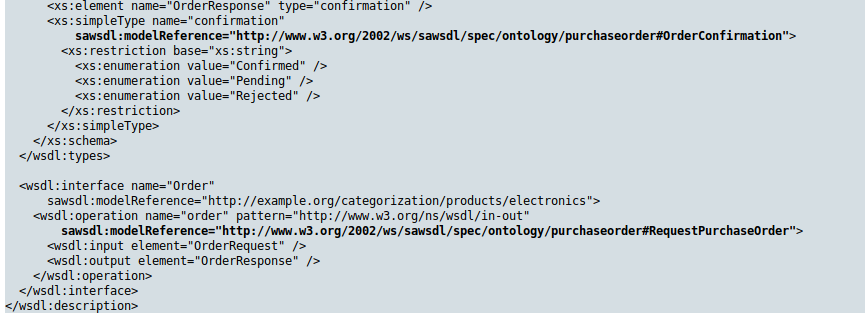
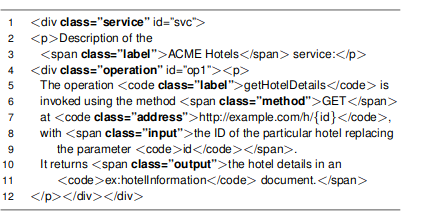
hRESTS
- Documentation lisible par l'homme et machine
- utilise microformat HTML
References
- Rodríguez, Carlos, et al. REST APIs: a large-scale analysis of compliance with principles and best practices. International Conference on Web Engineering. Springer, Cham, 2016.
- Pautasso, Cesare. RESTful web services: principles, patterns, emerging technologies. Web Services Foundations. Springer, New York, NY, 2014. 31-51.
- Samuel, John, and Christophe Rey. Integration of Multiple Heterogeneous and Autonomous Web Services using Mediation Approach: Open Challenges. Journal on Advances in Theoretical and Applied Informatics 2.2 (2016): 38-46.
- Kopecký, J., Gomadam, K., & Vitvar, T. Hrests: an html microformat for describing restful web services. IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology (2008), 1, 619–625. https://doi.org/10.1109/WIIAT.2008.379
- https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Representational_state_transfer
- https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Client%E2%80%93serveur
- https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/HATEOAS
- Apache Allowoverride
- .htaccess
- https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/CURL
- Form submission (W3C)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_Services_Description_Language
- https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_Services_Description_Language
- https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_Application_Description_Language
- https://www.w3.org/Submission/wadl/
- https://docs.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/technotes/tools/share/wsimport.html
- https://sourceforge.net/projects/wsdl4j/
- https://pypi.org/project/zeep/